Mar 1, 2013
Wireless Security (Know it all)
The ultimate hard-working desk reference: all the essential information, techniques and tricks of the trade in one volume
Download Link:
Wireless Security
Download Link:
Wireless Security
Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 4: Routing Protocols
Here is another very useful manual of Cisco Ip commands, I'm hosting .
Download Link:
Cisco IP, Routing commands
Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols
Here are some of the cisco IP most used commands in different configurations
CCNA 2 Final Exam Answers 2012
1. Which two statements are true for link-state routing protocols? (Choose two.)
Routers that run a link-state protocol can establish a complete topology of the network.
Routers in a multipoint network that run a link-state protocol can exchange routing tables.
Routers use only hop count for routing decisions.
The shortest path first algorithm is used.
Split horizon is used to avoid routing loops.
2.
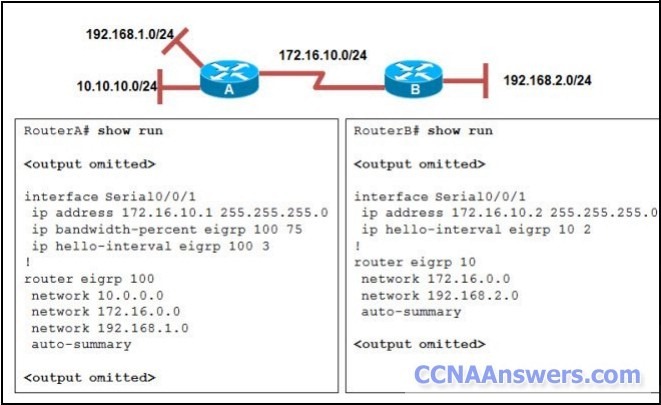
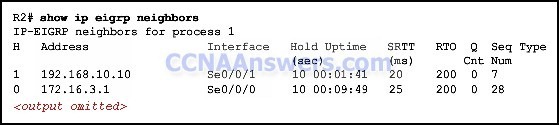
Refer to the exhibit. RouterA and RouterB cannot successfully exchange EIGRP routes. What is the problem?
The hello intervals do not match.
The autonomous system numbers do not match.
The no auto-summary command is missing from both routers.
The ip bandwidth-percent command is missing from RouterB.
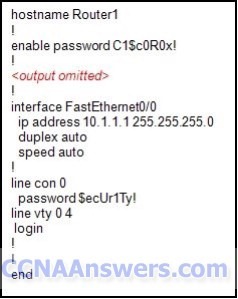
3.
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the partial output in the exhibit, why can users establish a console connection to this router without entering a password?
The login command was not entered on the console line.
The enable password should be an enable secret password.
No username and password combination has been configured.
Console connections cannot be configured to require users to provide passwords.
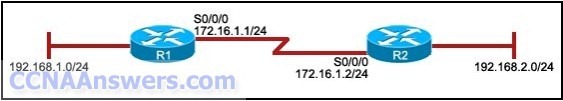
4.
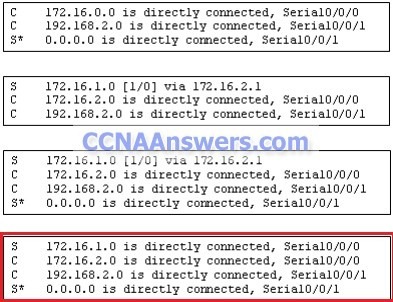
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator has run the following command on R1.
R1(config)# ip route 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.2
What is the result of running this command?
Traffic for network 192.168.2.0 is forwarded to 172.16.1.2.
This route is automatically propagated throughout the entire network.
Traffic for all networks is forwarded to 172.16.1.2.
The command invokes a dynamic routing protocol for 192.168.2.0.
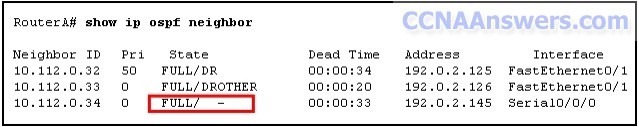
5.
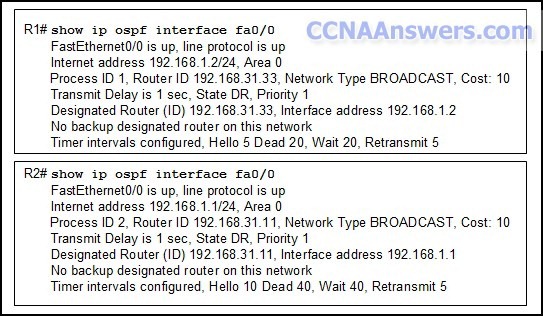
Refer to the exhibit. What does the state "FULL/ -" indicate?
The DR/BDR election is currently taking place.
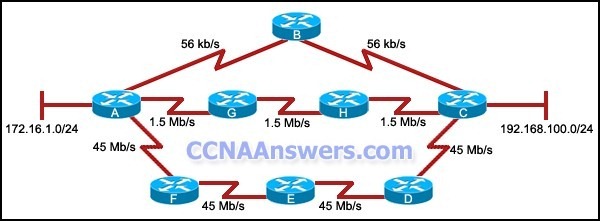
The router with router ID 10.112.0.34 and RouterA are on a point-to-point network.
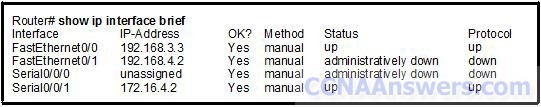
RouterA could not form a neighbor relationship with the router with router ID 10.112.0.34.
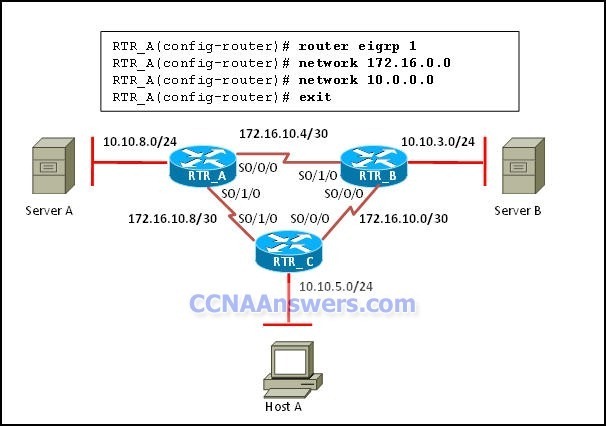
OSPF hello and dead timers between RouterA and the router with router ID 10.112.0.34 do not match.
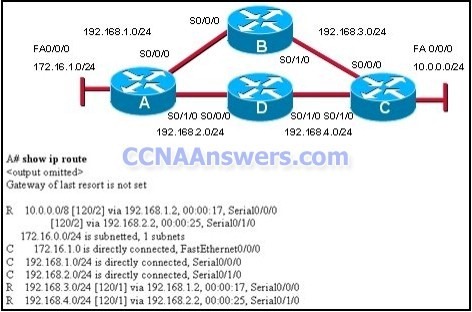
6. A router has learned about a network through static and dynamic routing processes. Which route will be used to reach network 192.168.168.0?
D 192.168.168.0/24 [90/2195456] via 192.168.200.1, 00:00:09, Ethernet0
O 192.168.168.0/24 [110/1012] via 192.168.200.1, 00:00:22, Ethernet0
R 192.168.168.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.200.1, 00:00:17, Ethernet0
S 192.168.168.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.200.1
7.
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured OSPF using the following command:
network 192.168.1.32 0.0.0.31 area 0
Which router interface will participate in OSPF?
FastEthernet0/0
FastEthernet0/1
Serial0/0/0
Serial0/0/1
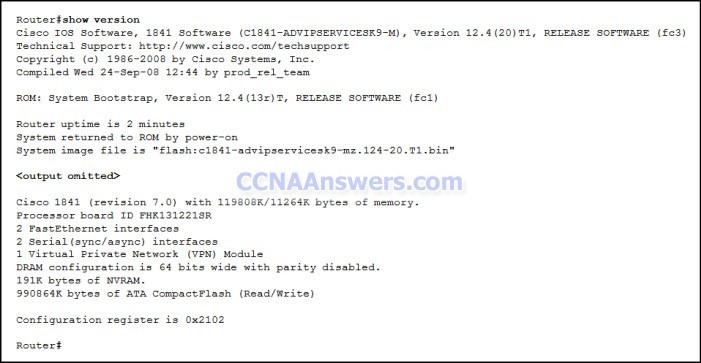
8. When would the IOS image held in ROM be used to boot the router?
during a file transfer operation
during a normal boot process
when the full IOS cannot be found
when the running configuration directs the router to do this
9.
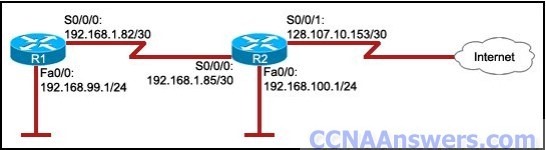
Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the show running-config output, which option correctly reflects the routes that will be listed in the R2 routing table?
10.
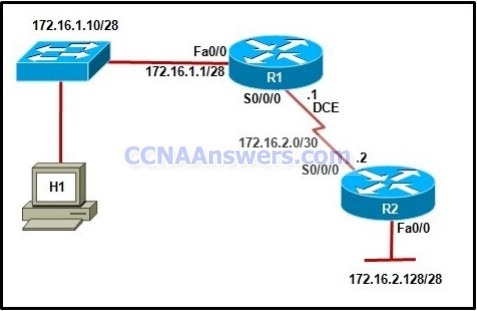
Refer to the exhibit. The hosts on the R1 LAN are unable to access the Internet. What is incorrectly configured?
the IP address of the Fa0/0 interface at R1
the IP address of the S0/0/1 interface at R2
the IP address of the S0/0/0 interface at R1
the subnet mask of the S0/0/1 interface at R2
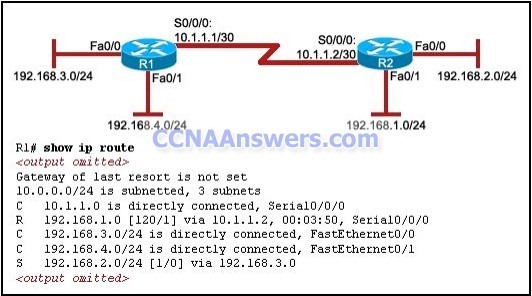
11.
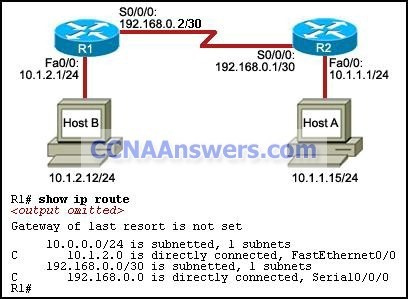
Refer to the exhibit. A ping from R1 to 10.1.1.2 is successful, but a ping from R1 to 192.168.2.0 fails. What is the cause of this problem?
There is no gateway of last resort at R1.
The serial interface between the two routers is down.
A default route is not configured on R1.
The static route for 192.168.2.0 is incorrectly configured.
12. What is a characteristic of classful routing?
support for VLSM
the use of 48-bit addresses
routing updates do not include a subnet mask
addresses that are typically entered in hexadecimal format
13. Which three statements are true regarding the encapsulation and de-encapsulation of packets when traveling through a router? (Choose three.)
The router modifies the TTL field, decrementing it by one.
The router changes the source IP to the IP of the exit interface.
The router maintains the same source and destination IP.
The router changes the source physical address to the physical address of the exit interface.
The router changes the destination IP to the IP of the exit interface.
The router sends the packet out all other interfaces, besides the one it entered the router on.
14. Which routing protocol maintains a topology table separate from the routing table?
IGRP
RIPv1
RIPv2
EIGRP
15.
Refer to the exhibit. The 10.4.0.0 network fails. What mechanism prevents R2 from receiving false update information regarding the 10.4.0.0 network?
split horizon
hold-down timers
route poisoning
triggered updates
16. Which two router component and operation pair are correctly described? (Choose two.)
DRAM – loads the bootstrap
RAM – stores the operating system
Flash – executes diagnostics at bootup
NVRAM – stores the configuration file
ROM – stores the backup configuration file
POST – runs diagnostics on hardware modules
17. Which multicast address does EIGRP use to send hello and updates packets?
224.0.0.5
224.0.0.6
224.0.0.9
224.0.0.10
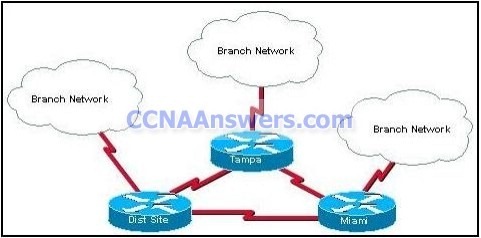
18.
Refer to the exhibit. The network consists of hundreds of routers branched from connected regional distribution sites using single area OSPF. Recent network failures caused packet flooding and route recalculations in all branch networks. What should the engineer do to minimize the effect of the routing instabilities?
Adopt RIPv2 which is not subject to packet flooding.
Implement static routing.
Implement a mix of routing protocols to contain the instabilities.
Change the topology to a heirarchical design which puts each branch network in its own area.
19. A network administrator is using an application that is monitoring packets on the network and sees an EIGRP update packet. What is the purpose of the update packet?
The packet is sent to discover neighbors within the EIGRP network.
The packet is sent to search for network devices within an EIGRP network.
The packet is used to propagate routing information within the EIGRP network.
The packet is used to send an unreachable reply to another router within the EIGRP network.
The packet is used to notify all routers that EIRGP has failed on one of the routers within the EIGRP network.
20. A router boots and enters setup mode. What is the reason for this?
The IOS image is corrupt.
Cisco IOS is missing from flash memory.
The configuration file is missing from NVRAM.
The POST process has detected hardware failure.
21. Which of the following are required when adding a network to the OSPF routing process configuration? (Choose three.)
network address
loopback address
autonomous system number
subnet mask
wildcard mask
area ID
22. Which prompt is used to allow a user to change the IP address of an interface on a router?
Router>
Router#
Router(config)#
Router(config-if)#
23.
Refer to the exhibit. Which path will traffic from the 172.16.1.0/24 network take to get to the 10.0.0.0/24 network?
ADC
ABC
It will load balance the traffic between ADC and ABC
It will send the traffic via ABC, and will use ADC as a backup path only when ABC fails.
24. Which statement correctly describes a feature of RIP?
RIP is a link-state routing protocol.
RIP uses only one metric—hop count— for path selection.
Advertised routes with hop counts greater than 10 are unreachable.
Messages are broadcast every 10 seconds.
25.
Refer to the exhibit. R1 and R2 are both configured with RIPv1. Beginning from global configuration mode, what comand or commands will eliminate RIP updates on the Ethernet segment of R2?
R2# configure terminal
R2(config)# router rip
R2(config-router)# passive-interface FastEthernet0/0
R2(config)# router rip
R2(config-router)# passive-interface FastEthernet0/0
R2# configure terminal
R2(config)# passive-interface FastEthernet0/0
R2(config)# passive-interface FastEthernet0/0
R2# passive-interface FastEthernet0/0
R2# configure terminal
R2(config)# interface FastEthernet0/0
R2(config-if)# passive-interface FastEthernet0/0
R2(config)# interface FastEthernet0/0
R2(config-if)# passive-interface FastEthernet0/0
26. In a complex lab test environment, a router has discovered four paths to 192.168.1.0/24 via the use of the RIP routing process. Which route will be installed in the routing table after the discovery of all four paths?
R 192.168.1.0/24 [120/3] via 192.168.110.1, 00:00:17, Serial0/1/0
R 192.168.1.0/24 [120/2] via 192.168.200.1, 00:00:17, Serial0/0/0
R 192.168.1.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.100.1, 00:00:17, Serial0/0/1
R 192.168.1.0/24 [120/4] via 192.168.101.1, 00:00:17, Serial0/1/1
27. Which two statements are true about the router ID in a single area OSPF network? (Choose two.)
Only the DR and BDR have a router ID.
A loopback interface is required to configure the router ID.
The router ID is used to uniquely identify each router in the OSPF routing domain.
Any interface, even one not participating in the OSPF routing process, can be used to determine the router ID.
If no loopback interfaces are configured, the router chooses the highest active IP address of any of its physical interfaces.
28. Which two statements about routing protocols are accurate? (Choose two.)
OSPF supports VLSM.
RIPv1 supports VLSM.
RIPv2 does not have a hop count limit.
EIGRP supports discontiguous network designs.
RIPv2 does not support discontiguous network designs.
29.
Refer to the exhibit. Which IP address and subnet mask can be configured on host H1 if it is to communicate with the network?
172.16.1.0 255.255.255.248
172.16.1.14 255.255.255.240
172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240
172.16.2.1 255.255.240.0
172.16.2.2 255.255.255.0
30.
Refer to the exhibit. What will happen when the router reloads?
It will boot into ROMMON mode.
It will ignore the start-up configuration file.
It will look for the start-up configuration file on the TFTP server.
It will attempt to load the start-up configuration file that is stored in NVRAM.
31. You have been asked to explain converged networks to a trainee. How would you accurately describe a converged network?
A network is converged when all routers have formed an adjacency.
A network is converged immediately after a topology change has occurred.
A network is converged when all routers flush the unreachable networks from their routing tables.
A network is converged after all routers share the same information, calculate best paths, and update their routing tables.
32. A router needs an IOS upgrade. Which component must be checked to make sure it meets the requirement for the new IOS?
boot ROM
Fast Ethernet ports
flash
serial ports
UART
CPU
33.
Refer to the exhibit. What information can be determined from the displayed output?
EIGRP packets are waiting to be sent to the neighbors.
The adjacencies between the routers are yet to be established.
The IP address 192.168.10.10 is configured at serial interface S0/0/1 of router R2.
Router R2 is receiving hello packets from a neighbor with the IP address 192.168.10.10 via the R2 S0/0/1 interface.
34. Which default EIGRP configuration must be modified to allow an EIGRP router to advertise subnets that are configured with VLSM?
split horizon
metric K values
autosummarization
hello and dead intervals
35. Which protocol is used by EIGRP to deliver and receive update packets?
FTP
RTP
TCP
TFTP
UDP
36.
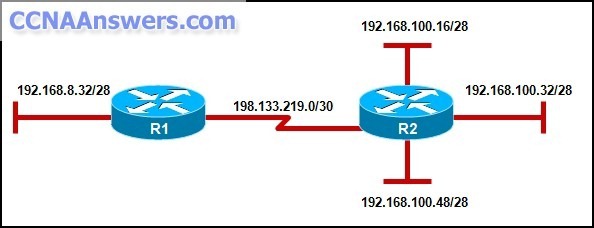
Refer to the exhibit. Which option will provide the configuration that is needed for router R1 to dynamically learn routes to the 192.168.100.16/28, 192.168.100.32/28, and 192.168.100.48/28 subnetworks?
with static routes
with a routed protocol
with a routing protocol
with directly connected routes
37. A network administrator is setting up a new router with a device name of Admin, an encrypted password of cangetin, and the IP address 192.168.1.22/29 assigned to the first FastEthernet interface. Which command sequence correctly configures this router?
Router(config)# hostname Admin
Admin(config)# enable secret cangetin
Admin(config)# interface fa0/1
Admin(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.22 255.255.255.248
Admin(config)# enable secret cangetin
Admin(config)# interface fa0/1
Admin(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.22 255.255.255.248
Router(config)# hostname Admin
Admin(config)# enable password cangetin
Admin(config)# interface fa0/1
Admin(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.22 255.255.255.248
Admin(config)# enable password cangetin
Admin(config)# interface fa0/1
Admin(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.22 255.255.255.248
Router(config)# hostname Admin
Admin(config)# enable secret cangetin
Admin(config)# interface fa0/0
Admin(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.22 255.255.255.248
Admin(config)# enable secret cangetin
Admin(config)# interface fa0/0
Admin(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.22 255.255.255.248
Router(config)# hostname Admin
Admin(config)# enable password cangetin
Admin(config)# interface fa0/0
Admin(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.22 255.255.255.248
Admin(config)# enable password cangetin
Admin(config)# interface fa0/0
Admin(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.22 255.255.255.248
38. All routers in a network are configured in a single OSPF area with the same priority value. No loopback interface has been set on any of the routers. Which secondary value will the routers use to determine the router ID?
The highest MAC address among the active interfaces of the network will be used.
There will be no router ID until a loopback interface is configured.
The highest IP address among the active FastEthernet interfaces that are running OSPF will be used.
The highest IP address among the active interfaces will be used.
39. What is the purpose of the TTL field within an IP packet header?
clears an unreachable route from the routing table after the invalid timer expires
prevents regular update messages from inappropriately reinstating a route that may have gone bad
removes an unreachable route from the routing table after the flush timer expires
limits the period of time or number of hops a packet can traverse through the network before it should be discarded
used to mark the route as unreachable in a routing update that is sent to other routers
40.
Refer to the exhibit. Host A is unable to access the Internet. What is the reason for this?
The IP address of host A is incorrect.
The default gateway of host A is incorrect.
The Fa0/1 interfaces of the two routers are configured for different subnets.
The subnet mask for the Fa0/0 interface of R1 is incorrect.
41.
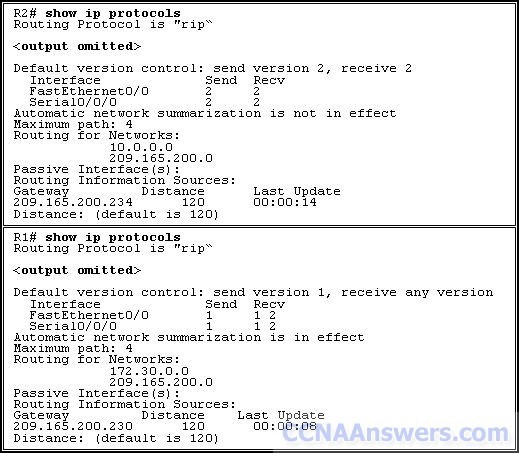
Refer to the exhibit. R1 and R2 are adjacent routers both running RIP. All interfaces on both routers are correctly configured and operational. Both routers are configured to include all connected interfaces in routing updates. R2 is not showing any routes from R1 in the routing table. What is the likely cause?
The adjacent interfaces are passive.
The distance of 120 exceeds 15 hops.
R2 will not accept version 1 updates from R1.
Routes are being summarized by R1 but not by R2.
42.
Refer to the exhibit. Router R2 is configured properly and all interfaces are functional. Router R1 has been installed recently. Host A is unable to ping host B.
Which procedure can resolve this problem?
Which procedure can resolve this problem?
Configure a static route on R1 using the IP address of the serial interface on R1.
Configure a default route on R1 with the exit interface Fa0/0 on R1.
Configure a static route on R1 using the IP address of S0/0/0 on R2.
Configure a default route on R1 using the IP address of Fa0/0 on R2.
43.
Refer to the exhibit. All routers are configured to use the EIGRP routing protocol with default settings, all routes are advertised on all routers, and the network is fully converged. Which path will the data take to travel between 172.16.1.0/24 and 192.168.100.0/24?
It will travel via A, B, and C.
It will travel via A, F, E, D, and C.
It will travel via A, G, H, and C.
The traffic will be load-balanced on all paths.
44.
Refer to the exhibit. A technician has configured the interfaces on the Router, but upon inspection discovers that interface FastEthernet0/1 is not functioning. Which action will most likely correct the problem with FastEthernet0/1?
A clock rate should be added to the interface configuration.
The subnet mask should be added to the interface configuration.
An interface description needs to be added to the interface configuration.
The no shutdown command needs to be added to the interface configuration.
45.
Refer to the exhibit. Host A is having problems accessing server A. All routers have the same EIGRP configuration as router RTR_A. What should be done so that host A can access server A?
Add the command no auto-summary on all routers.
Change the network statements to include a wildcard mask.
Adjust the EIGRP hello timers to account for the network delay.
Add the command eigrp log-neighbor-changes on all routers.
46.
Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R2 are directly connected through a FastEthernet link but cannot form a neighbor adjacency. What could resolve the problem?
The cost on R1 should be set higher.
The priority on R1 should be set higher.
The OSPF process ID numbers must match.
A backup designated router needs to be added to the network.
The hello and dead timers must be configured with the same values on both routers.
47.
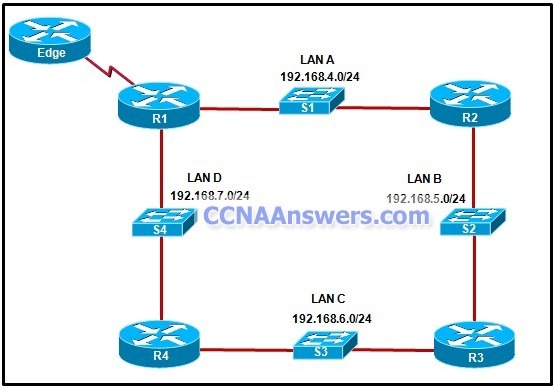
Refer to the exhibit. If the EIGRP routing protocol is used throughout the network, which IP address and mask prefix should be sent by router R1 to the Edge router as a result of manual summarization of LANs A, B, C, and D?
192.168.4.0/20
192.168.4.0/22
192.168.4.0/24
192.168.4.0/26
48.
Refer to the exhibit. Which summarization should R1 use to advertise its networks to R2?
192.168.1.0/24
192.168.0.0/24
192.168.0.0/22
192.168.1.0/22
49.
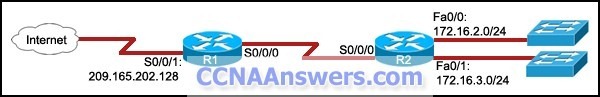
Refer to the exhibit. The command ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 S0/0/0 is run on router R2. What are the two results of this command? (Choose two.)
A static route will be updated in the routing table.
The traffic from the Internet will be directed to R2.
The traffic from the source network 172.16.0.0/22 will be blocked.
The route will be specified as the default route for all networks not defined in the routing table.
All the broadcasts will be forwarded via the S0/0/0 interface of R2.
50. What is the function of the OSPF LSU packet?
used to confirm receipt of certain types of OSPF packets
used to establish and maintain adjacency with other OSPF routers
used to request more information about any entry in the BDR
used to announce new OSPF information and to reply to certain types of requests
51. Which of the following are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
packet switching
microsegmentation
domain name resolution
path selection
flow control
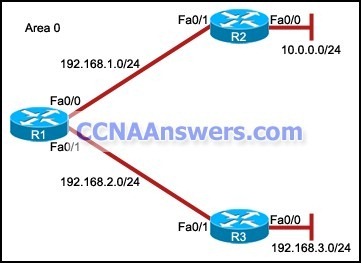
52.
Refer to the exhibit. The interfaces of all routers are configured for OSPF area 0. R3 can ping R1, but the two routers are unable to establish a neighbor adjacency. What should the network administrator do to troubleshoot this problem?
Check if the interfaces of the routers are enabled.
Check the hello and dead intervals between the routers.
Check the process ID of both routers.
Check if CDP is enabled on all the routers.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)